
Nursing School Studying, Nursing School Notes, Nursing Study
Hemodynamics can be tough. . . simply because there are so many interdependent factors that a nurse needs to know. In this episode, I share some of the KEY parameters the nurse should know as well as provide a free download of a hemodynamics cheat sheet. Free Download: Hemodynamics Cheat Sheet

hemodynamic monitoring College Nursing, Nursing School Studying
Hemodynamic stability is a requirement for any treatment plan, especially surgical procedures. Stable vital signs—such as blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen saturation—are generally a sign of adequate perfusion. When a patient is hemodynamically unstable, there's a higher risk of inadequate perfusion leading to organ failure, tissue.

Pin on Cardiology
The main purposes of hemodynamic monitoring are: to maintain adequate perfusion of the internal organs. early identification of preventable complications and life-threatening conditions (e.g., heart failure) to guide course of treatment and administration of fluids. to accurately determine the effectiveness of therapeutic interventions.

Pin on heart
Hemodynamic Monitoring: Overview and Practice Questions. Hemodynamic monitoring is an essential practice for assessing patients' cardiovascular health, especially in critical care settings. It involves real-time blood pressure measurements within the heart and blood vessels, alongside other parameters like cardiac output and oxygen delivery.

Preload Increased or Decreased it is acute and must be address or
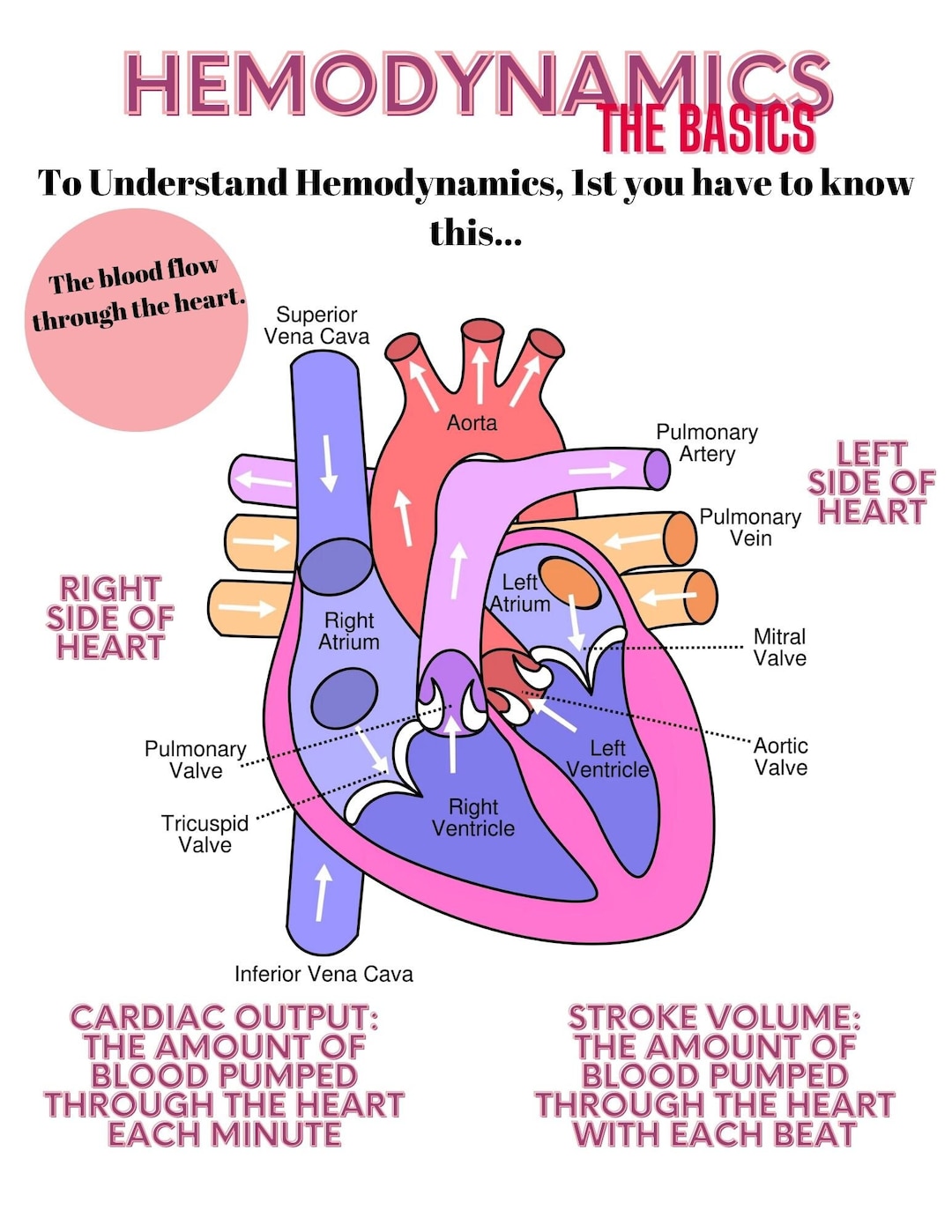
The cognitive domain knowledge includes: The definition of hemodynamics as the flow of blood as ejected from the heart to circulate throughout the body in order to effectively oxygenate the tissues of the body. The physiology and pathophysiology related to cardiac flow rate and cardiac output.

Cardiac Hemodynamics Badge Buddy Lidco Cheat Sheet Types of Etsy
Quality/Patient Safety. Renal. Sepsis. Staffing. Titration. Well-Being. View All Resources. Hemodynamic measurements must be accurate to ensure safe patient care and management. Learn important concepts related to invasive and noninvasive monitoring.

Pin on Nursing
Hemodynamic Parameters . Parameter . Calculation . Normal Value . Definition : Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) SBP + (DBP x 2) 3 . DBP + 1/3 pulse pressure . 70-105 mmHg : CVP . 0-8 mmHg . Reflects filling pressure of RV and mean pressure of systemic veins (i.e., venous return) PAP : 15-25 mmHg. 6-12 mmHg . Reflects RV afterload .
Hemodynamics Basics. Nurse Cheat Sheet Nursing (Download Now) Etsy
CCRN and TCRN Hemodynamics. Preload is volume measured by CVP (right) and PAOP (left). Afterload is pressure measured by PVR (lungs) and SVR (body). Afterload (SVR) is low only in distributive shock (neurogenic, anaphylaxis, sepsis). Cardiac index is cardiac output divided by BSA (2.5-4.0). Hypovolemic shock -High HR and SVR; replace fluids.

Nursing KAMP The Nurses Notes on Nursing » Cardiac Assessment Nurse
The pH of blood is a measurement of the concentration of hydrogen ions in the plasma. Normal range: 7.35 - 7.45 (mean 7.40) If a patient's pH is below 7.35, the patient is experiencing acidosis. If a patient's pH is above 7.45, the patient is experiencing alkalosis.

Hemodynamics Basics. Nurse Cheat Sheet Nursing Student Notes Etsy
In general terms, the topic of hemodynamics deals with flow and distribution of blood and fluids within the body. To maintain the correct amount of intravascular and extravascular volumes, the body must maintain both hydrostatic pressure and osmotic pressure. In vessels, hydrostatic pressure refers to the pressure pushing fluid out into the.

Hemodynamics Basics. Nurse Cheat Sheet Nursing (Download Now) Etsy
Hemodynamics. The study of forces involved in blood circulation. It is used to assess cardiovascular function in critically ill or unstable clients. The goal of using hemodynamics is to evaluate cardiac and circulatory function as well as evaluate response to interventions. Hemodynamic Parameters Heart rate.

My Level 1 Sheet covering Normal hemodynamics Pulse Pressure Cardiac
Hemodynamics is concerned with the mechanical and physiologic properties controlling blood pressure and flow through the body. A full discussion of hemo-dynamic principles is beyond the scope of this book. In this chapter, we present an overview of basic principles that are helpful in understanding hemodynamics. 1.

Hemodynamics! This is absolutely fabulous. Medical school inspiration
Normal cardiac output is between 4-8 L/min. However, there is no absolute normal cardiac output, only an adequate or inadequate. Cardiac output (CO) is calculated by multiplying the heart rate (HR) by the stroke volume (SV). CO =HR X SV. Cardiac index (CI) is the cardiac output adjusted for body surface area.

Free Nursing Cheatsheets Download Now Nurse, Nursing
hemodynamic monitoring tools, independent of their utility. Effectiveness of hemodynamic monitoring to improve outcome is limited to specific patient groups and disease processes for which proven effective treatments exist. Monitoring device will improve patient-centered outcomes when coupled to a treatment which, itself, improves outcome.

Nursing Mnemonics and Tips Archive Page 2 of 7 NCLEX Quiz
Normal ranges for 49 hemodynamic parameters. Equations for computing parameters, where applicable. Normal lab values for hematocrit (Hct) and hemoglobin (Hgb) values for men and women, as well as adult lactate values. Physio-relationship graphic for preload, afterload, and contractility. Quick-reference graphic for transpulmonary thermodilution.

Hemodynamics Cheat Sheet
Establish the zero level and balance transducer. Confirm the scale of the recording. -40 mmHg for RHC, 200 mmHg for LHC. Collect hemodynamics in a systematic method using established protocols. Critically assess the pressure waveforms for proper fidelity. Carefully time pressure events with the ECG. Review the tracings for common artifacts.