
PPT Lecture 7 Hypothetical Deductive Method PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5481676
Hypothetico-deductive Method Anton E. Lawson* School of Life Sciences, Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ, USA Thehypothetico-deductive(HD)method.
5 Research Questions and Aims Global Health Research Designs and Methods
Thus Whewell's philosophy of science cannot be described as the hypothetico-deductive view. It is an inductive method; yet it clearly differs from the more narrow inductivism of Mill. Whewell's view of induction has the advantage over Mill's of allowing the inference to unobservable properties and entities, and for this reason is a more.

SOLUTION The hypothetico deductive method 5th edition Studypool
The role of hypothetical thinking in the HD method for testing hypotheses is obvious—it is, after all, in the name hypothetico-deductive. However, the extent to which hypothetical thinking supports other scientific practices may be less evident.

Basics of psychology Class 11 Chapter 1
The hypothetico-deductive method is one of the mainstays of scientific research, often regarded as the only 'true' scientific research method. This area fuels intense debate and discussion between many fields of scientific specialization. Concisely, the method involves the traditional steps of observing the subject, in order to elaborate upon.
PPT Lecture 7 Hypothetical Deductive Method PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5481676
It is true that during a hypothetico-deductive investigation, the researcher should try to be as objective and as unemotionally "connected" to the respondents as possible. In an ideal world, one could test the variables in highly controlled or fully controlled circumstances. The researcher would have two clone groups, one where one variable.

Diagram describing iterative nature of the hypotheticodeductive method Download Scientific
The standard starting point for a non-inductive analysis of the logic of confirmation is known as the Hypothetico-Deductive (H-D) method. In its simplest form, a sentence of a theory which expresses some hypothesis is confirmed by its true consequences. As noted in section 2, this method had been advanced by Whewell in the 19 th century,.

An idealized version of the hypotheticodeductive model of the... Download Scientific Diagram
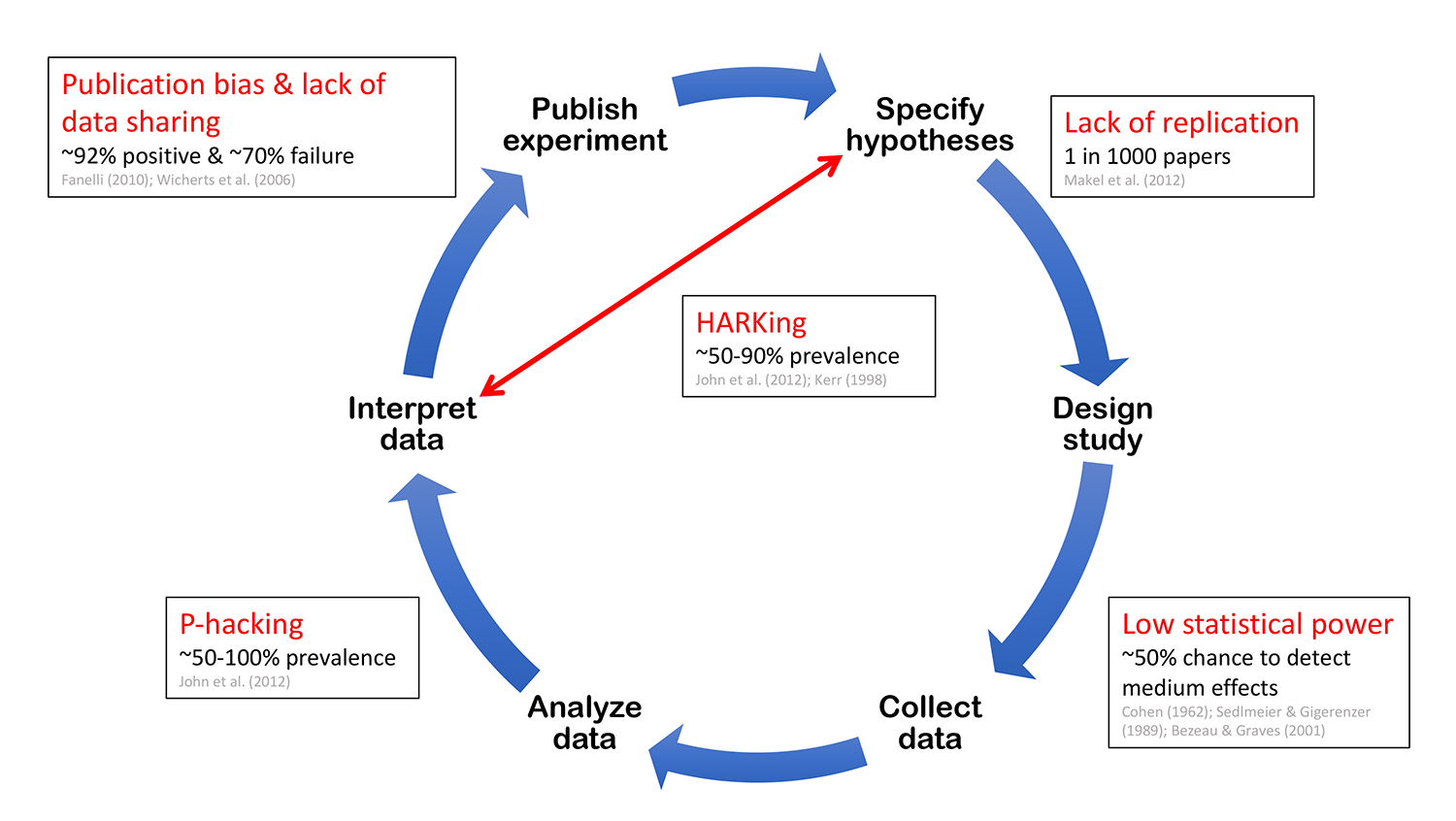
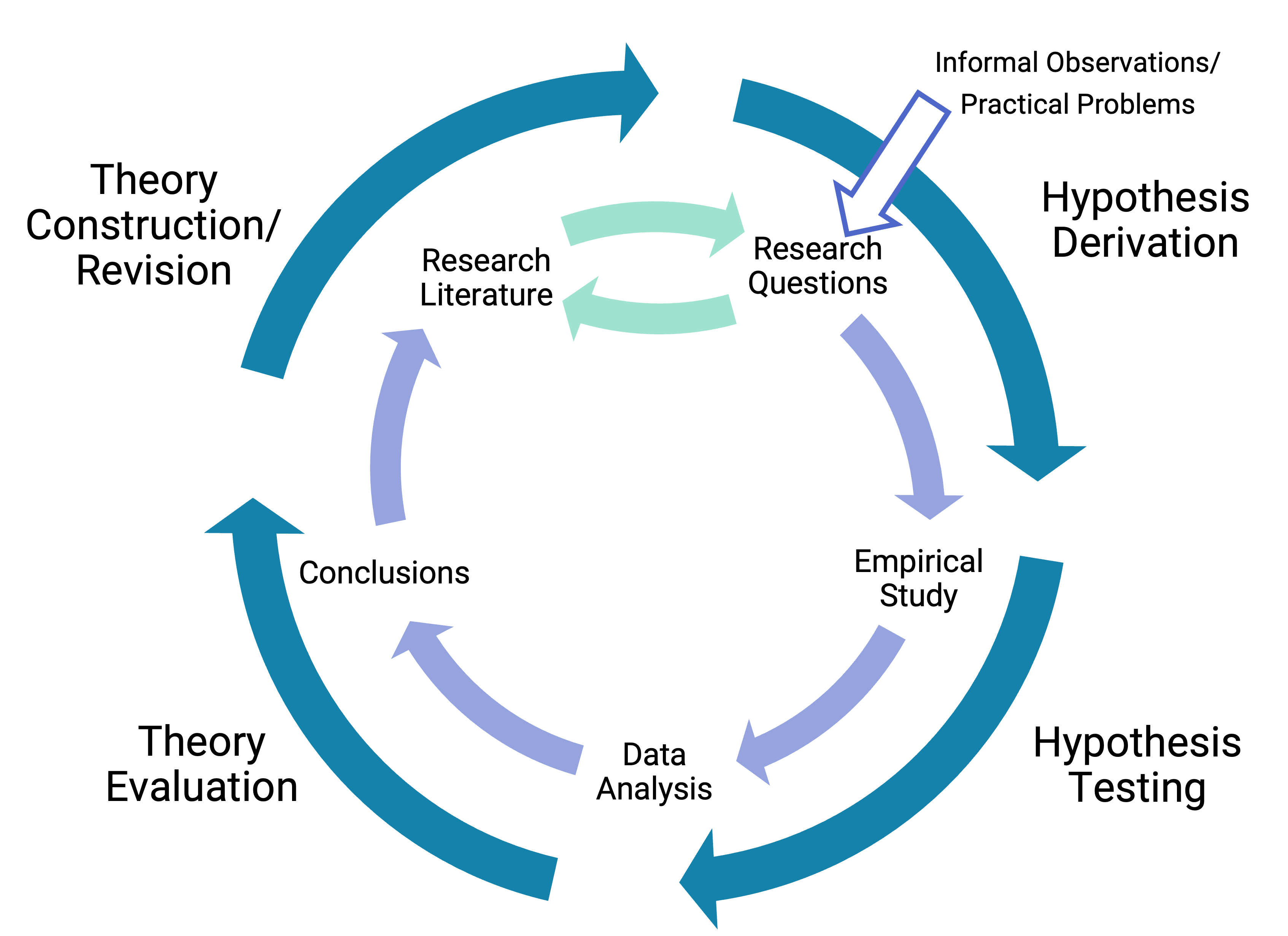
The hypothetico-deductive (HD) method, sometimes called the scientific method, is a cyclic pattern of reasoning and observation used to generate and test proposed explanations (i.e., hypotheses and/or theories) of puzzling observations in nature. The goal of the method is to derive useful knowledge - in the sense that causes are determined.

Hypotheticodeductive model
The hypothetico-deductive (H-D) method is reported to be common in information systems (IS). In IS, the H-D method is often presented as a Popperian, Hempelian, or natural science method. However, there are many fundamental differences between what Popper or Hempel actually say and what the alleged H-D method per Hempel or per Popper means in IS.
Chapter 11 Theory in Psychology A Modern Guide to Understanding and Conducting Research in
Deductive reasoning is commonly used in scientific research, and it's especially associated with quantitative research. In research, you might have come across something called the hypothetico-deductive method. It's the scientific method of testing hypotheses to check whether your predictions are substantiated by real-world data.

What is hypothetico deductive approach to research? YouTube
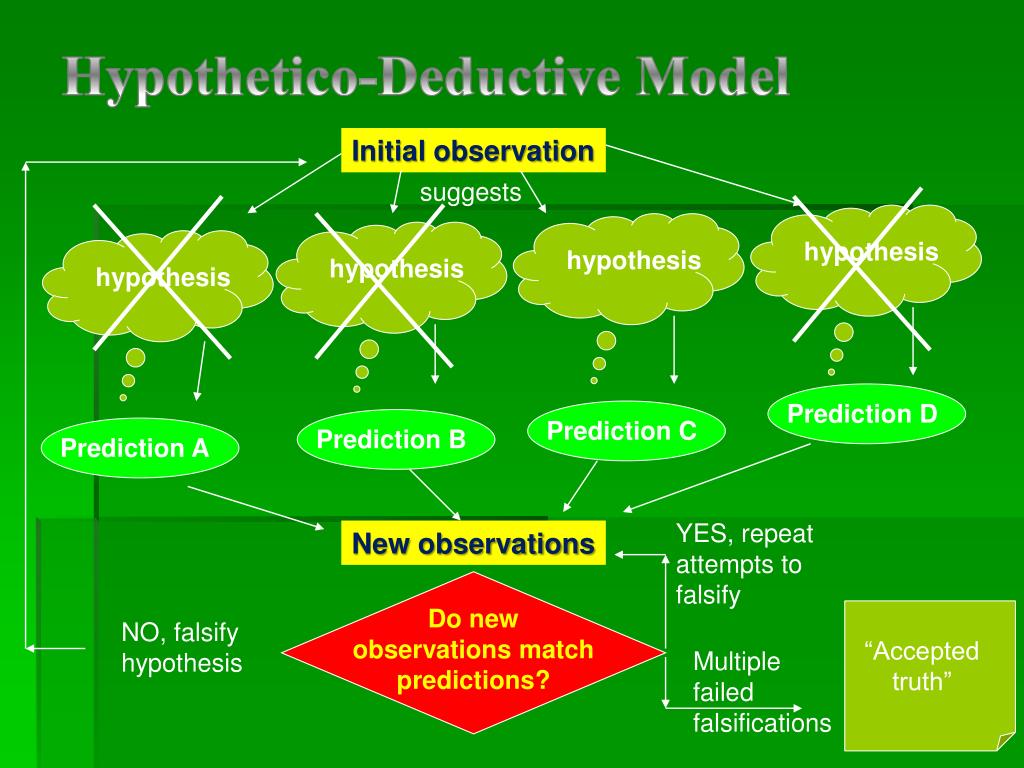
Search for: 'hypothetico-deductive method' in Oxford Reference ». The method particularly associated with a philosophy of science that stresses the virtues of falsification. Most simply, a hypothesis is proposed, and consequences are deduced, which are then tested against experience. If the hypothesis is falsified, then we learn from the.
Hypotheticodeductive MethodMicroeconomic Study
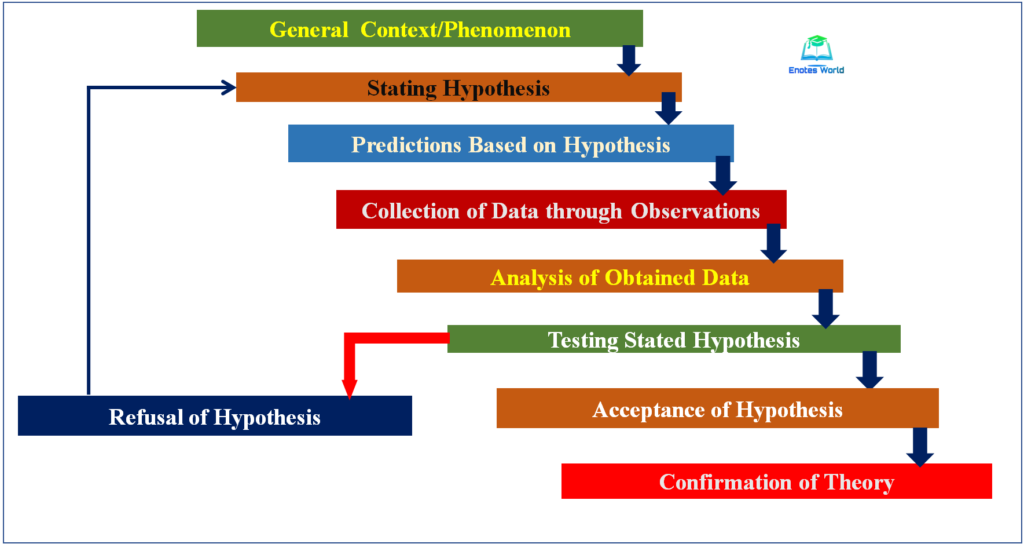
Hypothetico-Deductive Method. Definition: The hypothetico-deductive method is an approach to research that begins with a theory about how things work and derives testable hypotheses from it. It is a form of deductive reasoning in that it begins with general principles, assumptions, and ideas, and works from them to more particular statements.

Lecture 08A HypotheticoDeductive Method (Part I) YouTube
Summary. As the name indicates there are at least two parts to the hypothetico-deductive (h-d) method: a hypothetico part in which a hypothesis or theory, arising from whatever source, is proposed for test, and a deductive part in which test consequences are drawn from the hypotheses. Unmentioned in the name of the method is a crucial third.
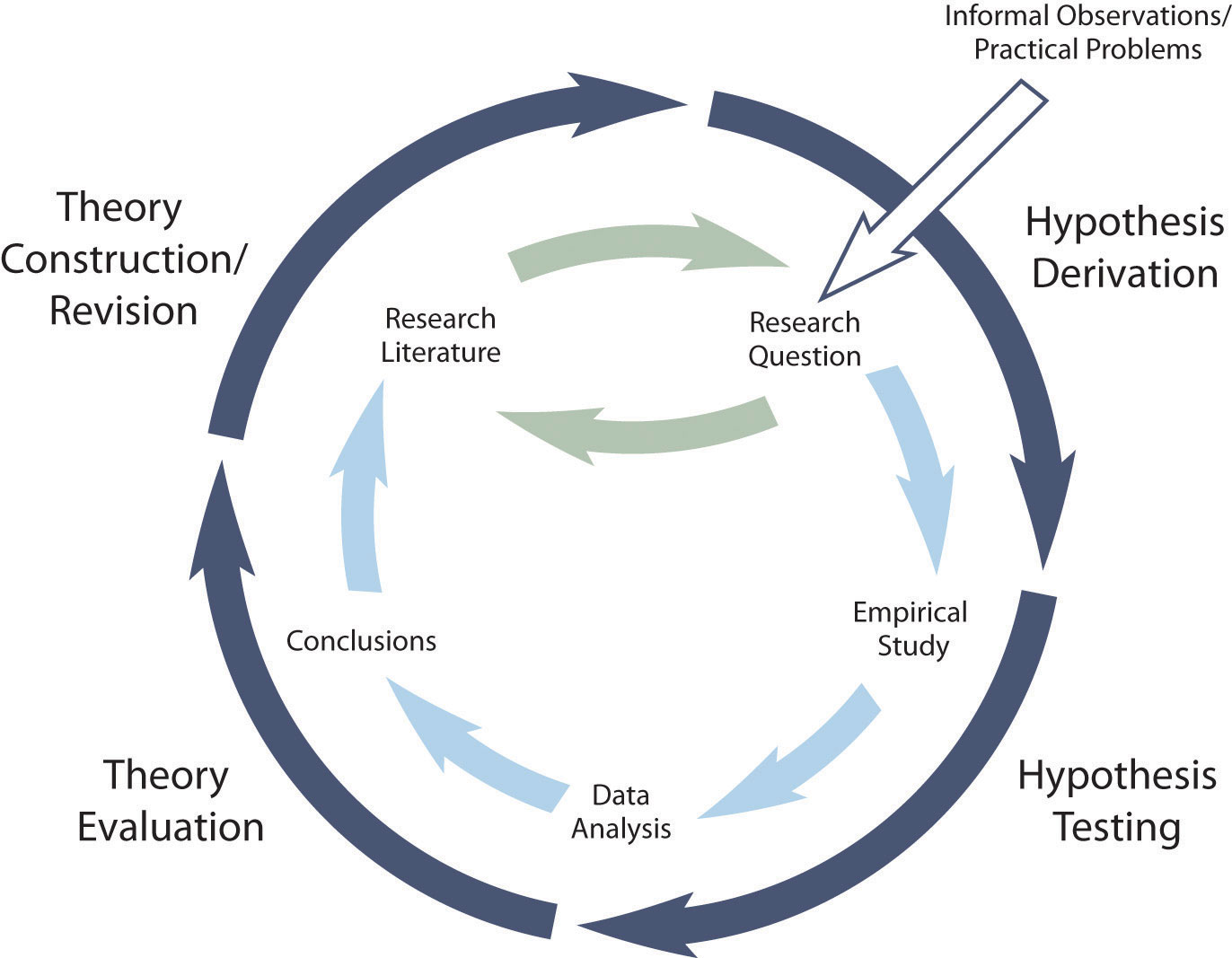
4.3 Using Theories in Psychological Research Research Methods in Psychology
For these scholars, the method in the Rules is a priori and proceeds from causes to effects, while the method in Discourse VI is a posteriori and proceeds from effects to causes (see Clarke 1982). The latter method, they claim, is the so-called "hypothetico-deductive method" (see Larmore 1980: 6-22 and Clarke 1982: 10).

Relationship between the hypotheticodeductive model of clinical... Download Scientific Diagram
In conclusion, the much-used hypothetico-deductive method for teaching clinical reasoning did relatively well in our study. Tentative explanations have been raised but further research is required to explore which approach works better and under which conditions. New methods, such as self-explanation, need further scrutiny.
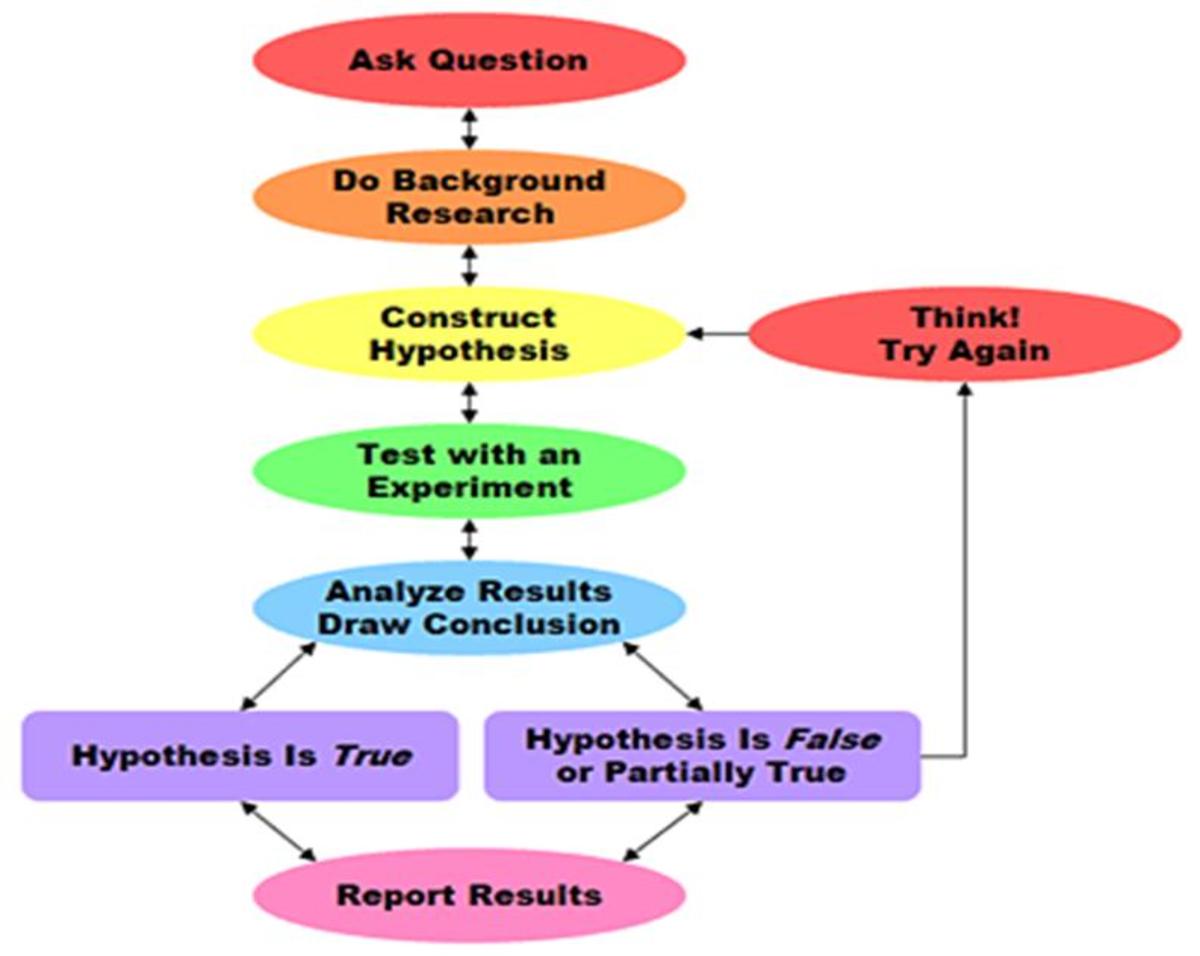
HypotheticoDeductive Method in Business Research HubPages
The hypothetico-deductive (HD) method is the term that philosophers and methodologists of science use to refer to the scientific practice of validating theories by means of formulating hypotheses (premises), and deriving and testing conclusions. According to an early proponent of the method, John Stuart Mill, political economy must be.

Metodo Deductivo
The meaning of HYPOTHETICO-DEDUCTIVE is relating to, being, or making use of the method of proposing hypotheses and testing their acceptability or falsity by determining whether their logical consequences are consistent with observed data.